If nothing else, the focus on energy efficiency over the last several years has highlighted two main factors:
• Industrial facilities are the biggest users of energy;
• Motors and drives account for he majority of energy used in industrial facilities.
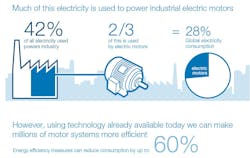
Drives, in particular, have been a major area of focus, as electric drives are used to regulate the speed and power consumption of electric motors. Industrial electric motors are said to account for about 25 percent of all the electricity consumed worldwide. Furthermore, reducing a motor’s speed by half using a drive can reduce the energy it consumes to one-eighth of its consumption at full speed.
With this is mind, it makes sense that motors and drives have been the principal focus for energy efficiency improvement efforts across industry. And now that these efficiency projects have been under way for some time, reports are starting to surface that estimate just how much is being saved.
One such report has been released by ABB, and it states that about 310 million megawatt-hours of electric power was saved by ABB drives in 2011. This savings in electric power is equivalent to approximately $34 billion in electricity costs for U.S. customers, according to ABB. This savings estimate is based on a comparison of the average electricity consumption in applications with and without drives.
“The future potential for energy and cost savings is enormous, since only about 10 percent of industrial motors are currently combined with electric drives,” said Ulrich Spiesshofer, member of the Group Executive committee and head of ABB’s Discrete Automation and Motion division. “Using energy more efficiently will remain, for a significant time, the biggest opportunity available to cut energy consumption, as well as costs and emissions.”
See other energy efficiency-related articles at AutomationWorld.com:
Leaders relevant to this article: